Introduction
A Health Savings Account (HSA) is a custodial or tax-exempt trust account created for or by individuals covered under High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs) to save for qualified medical expenses. Contributions are made into the account by the employer or their individual and are limited to a certain amount each year & you must be an eligible individual to qualify for an HSA. You can save money in your HSA account before taxes and use the funds to pay for eligible health care expenses. HSAs can also help you save for retirement, when you can use the funds to pay for general living expenses without penalty.
Permission or authorization is not needed from the IRS to establish an HSA. You can set up HSA with a trustee. A qualified HSA trustee can be a bank, an insurance company, or anyone already approved by the IRS. The HSA can be established through a trustee who is different from your health plan provider.
Required qualification for an HAS contribution
To be an eligible individual and qualify for an HSA contribution, you must meet the following requirements.
⦁ You should have qualified high deductible health plan (HDHP).
⦁ You must not have other health coverage except what is permitted.
⦁ You cannot be enrolled in Medicare.
⦁ You can’t be claimed as a dependent on someone else’s tax return.
If you meet these requirements, you are an eligible individual even if your spouse has non-HDHP family coverage, provided your spouse’s coverage doesn’t cover you. You must remain an eligible individual during the testing period in order to take advantage of the last-month rule.
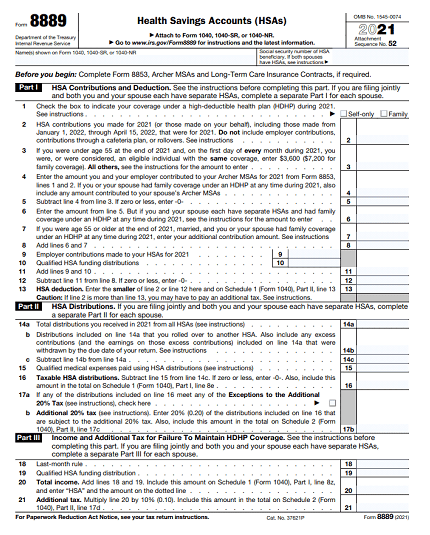
The Form 8889 contain three parts and Part I reports HSA contribution Part II Distribution and Part III reports Income and Additional Tax for Failure to Maintain HDHP Coverage.
HSA Contribution
Individual who are eligible can contribute to an HSA. For an employee’s HSA, the employee’s employer or both employee & employer can contribute employee’s HSA in the same year. HSA established by a self-employed or unemployed individual, the individual can contribute. Family members or any other person can make contributions on behalf of an eligible individual. Contributions of stock or property aren’t allowed. Contributions to an HSA must be made in cash.
HSA Deduction
The maximum amount that can be contributed to your HSA depends on the type of HDHP coverage you have. If you have self-only coverage, your maximum contribution is $3,600. If you have family coverage, your maximum contribution is $7,200. If taxpayer age is 55 or more at the end of your tax year, you can make an additional contribution of $1,000.
Part I of Form 8889 reports HSA Contributions and Deduction
Line one must check whether taxpayer covered by self HDHP or covered under family HDHP, Second line reports the contribution made to the particular plan from January 1 through April 15. And third columns repots maximum deductable values such as if u have self than it take $3600 and if you’re family coverage maximum up to $7200(Plan coverage changes every tax year or colander year) If taxpayer age is 55 or more than that you can avail extra $1000.
Line 6 reports Spouses who have separate HSAs and had family coverage under an HDHP at any time during 2021 If you are treated as having family coverage for each month, divide the amount on line 5 equally between you and your spouse, unless you both agree on a different allocation Enter your allocable share on line 6.
Line 7 reports Additional contribution amount includes certain conditions and Line number 9 and 10 reports Employer contribution of HSA and Qualified HSA funding distribution. A distribution from your traditional IRA or Roth IRA to your HSA in a direct trustee-to-trustee transfer is called an HSA funding distribution. Note that these funds are not being distributed from your HSA, but rather are being distributed from your IRA and contributed to your HSA. Enter this amount on line 10.
If you contributed more to your HSA than is allowable, you may have to pay an additional tax on the excess contributions. Excess contribution need to show under line number 13
Part II of Form 8889 reports HAS distribution
Line number 14a reports total distribution you received during the tax period and 14b any distributions you received in 2021 that qualified as a rollover contribution to another HAS.
Line 15 reports total qualified medical expenses not reimbursed by insurance or other coverage and that you incurred after the HSA was established. Do not include the distribution of an excess contribution taken out after the due date, including extensions, of your return even if used for qualified medical expenses.
Line 17a and 17b reports additional tax of additional distribution made exception to the additional tax is 1.Dies.
- Becomes disabled, and
- Turns age 65.
Part III reports Income and Additional Tax for Failure to Maintain HDHP Coverage
Use Part III to figure any additional income and adjustments to income that must be reported on Schedule 1.